
Technical Article
The Texas Blackout is a Man-Made Disaster of Epic Proportions
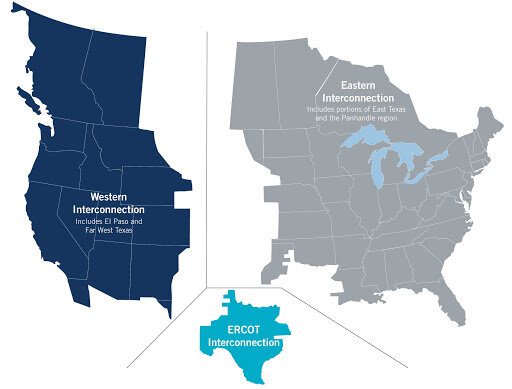
Since the discovery of oil at Spindletop in 1901, Texas has held a strong claim to the title of America’s energy capital. Based on pre-pandemic production, Texas would rank among the top five countries in the world in terms of oil and gas production. Moreover, it is the top wind power producer in the US and the number two state market for solar. Founded as an independent Republic, the Lone Star State proudly operates its own independent electric power system, which serves 90% of the state’s electric load.
As my wife and I melted snow this week to flush the toilets in our 100-year-old East Austin home, located a short walking distance from the Texas State Capitol, it occurred to me more than once that the slope from pride to hubris is slippery and treacherous, much like the steps out our front door and streets all across our frozen and paralyzed state. For three days we had no heat or power as overnight lows fell to 5°F (-15°C). A week later, line crews are still restoring power to some homes and businesses.
Largest Insurance Claim Event in State History
Based on a cruel combination of metrics, the Arctic air that wobbled down from the North Pole and parked itself over Texas is a clear contender for the worst winter storm in a century. In terms of severity, few winter storms over the past 100 years have notched colder freezing temperatures. In terms of duration, few freeze events have lasted as long without breaking. In terms of extent, for the first time ever all 254 counties in Texas—a state that is two time zones wide—were simultaneously subject to a winter storm warning. It was colder in Dallas, Texas, than in Anchorage, Alaska.
This was a record-breaking storm that likely inflicted record insured losses. Insurance claims associated with Hurricane Harvey, which in August 2017 dropped 40 to 60 inches of rain in and around Houston, totaled about $20.1 billion after adjusting for inflation. Many insurance industry experts and associations already project that this winter storm will constitute the largest insurance claim event in Texas history, both in terms of the cumulative number and the total value of claims.
It is important that incident investigators and politicians, in the state’s capital and the nation’s, acknowledge and wrestle with the extent to which this was a man-made disaster. Scientists, insurance providers, Fortune 500 companies, and hedge fund managers are well aware of the risks associated with a business-as-usual approach to energy. Some will argue that this is first and foremost a natural disaster. However, the root causes of increasingly severe and extreme weather are proudly made right here in Texas, which is by far the nation’s leading emitter of carbon dioxide.
What’s Past is Prologue
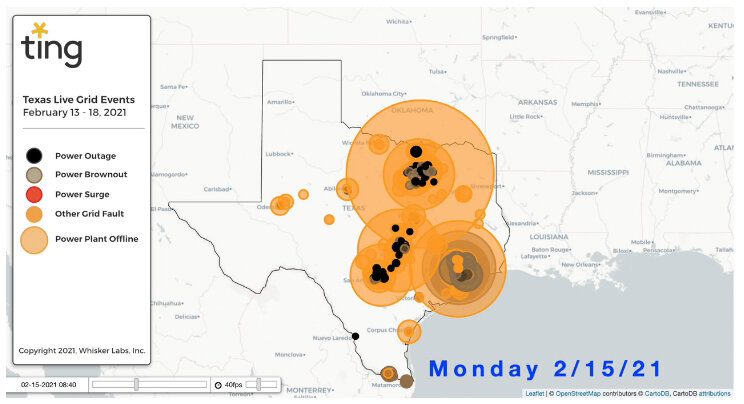
The electrical blackouts and cascading system failures associated with the 2021 Valentine's Day weekend Arctic blast were both predicted and entirely avoidable. The power system operated by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) and the state’s natural gas infrastructure suffered similarly in February 2011. Reading the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) report, "Outages and Curtailments During the Southwest Cold Weather Event of February 1–5, 2011: Causes and Recommendations," we see that the past is prologue for the recent failures.
In February 2011, extreme cold weather caused energy demand to peak even as thermal power plants and natural gas supplies froze up. In order to protect the power system, ERCOT had to call on load-serving entities to shed load by implementing rolling blackouts across their service territories. Over 4 million people were affected and it was many days before heat and power were restored to all customers.
In 2011, Rick Perry was the governor of Texas. One presumes he read the FERC report or knew of its existence. We know for a fact that the winterization and operational measures called for in the report were not implemented. Oops. In reward for a job well done, Perry was awarded leadership of the Department of Energy—a department he famously could not name during a 2012 presidential campaign debate.
Texas politicians, utility regulators, power generators, and grid operators had advance warning regarding the systemic weaknesses associated with un-winterized power generation and natural gas assets. The blackouts and cascading failures associated with the recent deep freeze represent an epic and unconscionable failure of leadership, management, and market design.
ERCOT Market Worked as Designed
In a Harvard Electric Policy Group report, William Hogan, the architect of ERCOT’s energy-only market, notes that, “ERCOT employs an open wholesale market as the basis of short-term reliable electric supply as well as for long-term investments to maintain reliability in the future.” Scarcity pricing is central to the design of the ERCOT market, which does not include capacity payments, a common mechanism in other wholesale electricity markets for ensuring resource adequacy in the event of an emergency. Faced with a predictably severe cold-weather event, the ERCOT market failed to supply electricity reliably.
Millions of people suffered. Rate payers, wage earners, property owners, businesses, and retail electric providers lost billions of dollars. Some will never recover. Meanwhile, the ERCOT market provided record returns for some generators.
For more than 100 hours, energy traded on ERCOT at the market cap price of $9,000 per megawatt-hour. Based on daily load profiles, energy-only revenues following the statewide blackout were likely on the order of $10 billion per day or $40 billion over four days. By comparison, analysts at Houston-based Wood Mackenzie estimate that ERCOT’s energy-only market produced $10 billion in revenues in all of 2020.

Human Costs of Privatizing Profits While Socializing Risk
The ERCOT market is in many ways the pride of Texas, the embodiment of the state’s independent go-it-alone spirit and its laissez-faire approach to an unregulated free market. By and large, this market has served Texans well, producing low energy costs and the nation’s leading market for renewable energy. This same system also failed the state’s residents and businesses spectacularly in a moment of great need.
Those hit hardest by the pandemic—people of color, poor and working-class households, and small businesses—will also disproportionately bear the brunt of the burden associated with this winter storm.
While an Arctic blast settled over Texas, plunging its residents into darkness and freezing critical infrastructure and supply chains, our populist Senator flew to Cancun, Mexico, for some fun in the sun. Other state leaders offered red meat to their political base, blaming wind turbines, ignoring facts on the ground, sidestepping their own culpability, and otherwise tilting at culture-war windmills. Former governor Perry put forth the straw man that, “Texans would be without electricity for longer than three days to keep the federal government out of their business.” Happily, one presumes.
One wonders whether Rick Perry himself spent three or more days without electricity during a once-in-a-century winter storm. Watching his breath hang in the air. Watching the thermostat fall. Waiting helplessly for pipes to burst. Taking shelter at a crowded warming center during a virulent pandemic. Raging against the darkness as flames destroyed memories and futures. Sliding into unconsciousness inside a running car parked within a closed garage. Losing loved ones to a frozen slumber.
A version of this blog post originally appeared as on OpEd in pv magazine USA. Photos courtesy of the author.

